The structure of the cell membrane is crucial in helping the cell maintain its homeostasis. Recall that homeostasis is the fundamental process by which living organisms maintain a stable internal environment, despite external changes or fluctuations. It involves the regulation and balance of various physical and chemical factors within an organism’s body to ensure optimal conditions for cells and overall health. These factors include such things as temperature and pH.
In the context of the cell membrane, homeostasis refers to the cell’s ability to keep its internal environment stable and suitable for cellular functions. The cell membrane acts as a key player in maintaining this equilibrium. It regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell to control the concentration of essential molecules, manage water levels, and protect against harmful invaders, thus ensuring that the cell’s interior remains in a state of balance and harmony.
So, in simpler terms, homeostasis is like a cell’s way of keeping things “just right” inside itself, and the cell membrane is the guardian that makes sure everything stays balanced by controlling what comes in and goes out.
Let’s dive in a little deeper…
The Cell Membrane: Guardian of the Cell’s Galaxy
Imagine your body is like a bustling city, and each of the cells in your body is like a tiny house. These cells have to keep their environments just right to stay healthy and do their jobs. The cell membrane is like the gatekeeper of the cell, making sure everything stays balanced. This balance is called homeostasis, and it’s super important!
The Cell Membrane Structure
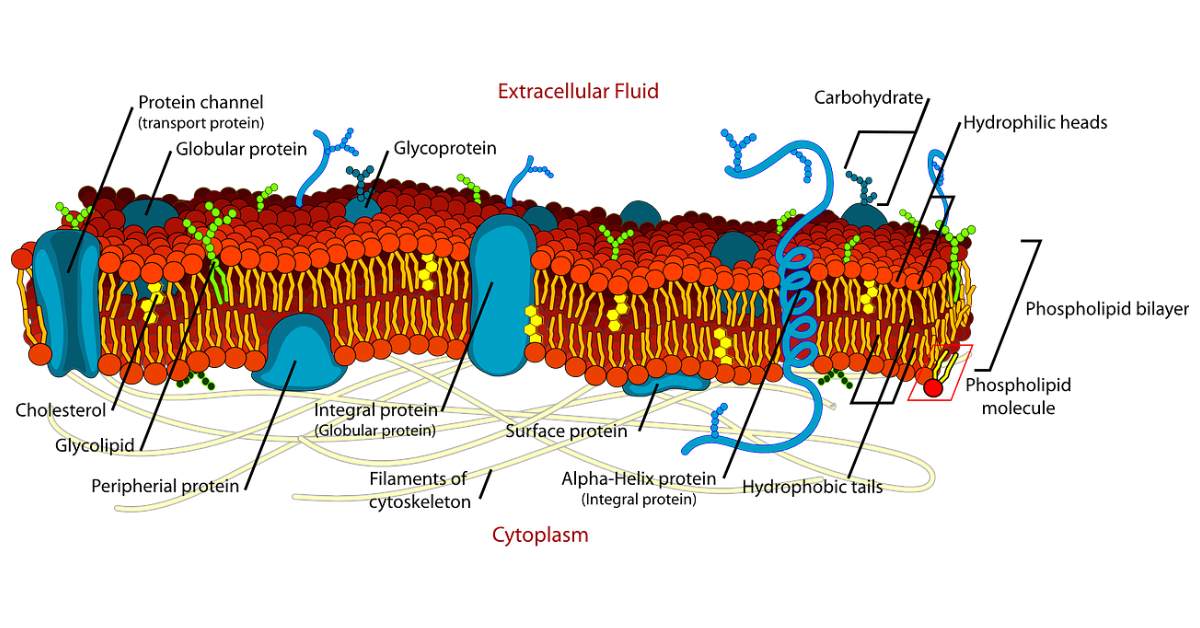
Before we get into how the cell membrane keeps things balanced, let’s talk about what it looks like. The cell membrane is like a flexible, super-thin wall around the cell, kind of like the skin of a bubble. It’s made up of special molecules called phospholipids. These molecules have two parts – a head and a tail.
Imagine that the heads are like magnets for water, and the tails are scared of water. So, the heads point outwards, facing the watery environment outside and inside the cell, while the tails hide inside. This helps to form a protective barrier.
Controlling What Goes In and Out
One of the most important jobs of the cell membrane is to control what goes in and out of the cell. Think of it as a bouncer at a club, making sure only the right people get in. The cell needs to let in nutrients like sugars and oxygen, and it needs to get rid of waste products. At the same time, it has to keep the bad stuff out, like harmful bacteria or toxins.
To do this, the cell membrane has tiny doors and windows. These doors and windows are like special proteins that act as gatekeepers. They have specific shapes that only allow certain things to pass through. For example, glucose has its very own key that fits perfectly into a protein door. So, the door opens, and glucose can enter the cell. It’s like a secret handshake!
Balancing Water Levels
Water is super important for cells, just like it’s important for you. Cells need a balanced amount of water to work properly. If too much water goes in, the cell can burst like an overfilled balloon. If too much water goes out, it can shrivel up like a raisin.
The cell membrane helps control the water balance using something called osmosis. This is like a water tug-of-war. If there’s more water outside the cell, water will try to rush in. But the cell membrane can let a little bit of water in through special water channels, or it can pump water out to keep things balanced. It’s like a water dance party with the cell membrane as the DJ!

Keeping the Right Chemicals Inside
Inside the cell, there are all sorts of important chemicals and structures. The cell membrane makes sure that these important things stay inside and don’t escape. Imagine your room is full of toys, and you don’t want them to roll out into the hallway. The cell membrane is like the closed door that keeps everything inside.
Staying in Touch with the Neighbors
Cells often need to communicate with each other, and the cell membrane plays a part in this too. On the surface of the cell membrane, there are special proteins that act like cell phones, allowing cells to send and receive messages. This communication helps the cells work together to maintain balance in the body.
Adapting to Change
The environment around your cells can change, and your cells need to adapt. For example, if you’re running and your muscles need more oxygen, the cell membrane can open up more oxygen doors to let in extra oxygen. This helps your muscles work better and keep you going. It’s like your cells have a built-in thermostat that adjusts to the situation.
The Cell Membrane and Homeostasis – Conclusion
So, the cell membrane is like the cell’s superhero, making sure everything inside is just right and that the cell can adapt to changes. It helps maintain balance, which we call homeostasis, by controlling what goes in and out, keeping the right chemicals inside, managing water levels, and allowing cells to communicate with each other. Thanks to the cell membrane, our cells can stay healthy and work together to keep our whole body in harmony.